Ethylisopropyltryptamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | EiPT; N-Ethyl-N-isopropyltryptamine |
| Routes of administration | Oral[1] |
| Drug class | Psychedelic drug; Serotonergic psychedelic |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Duration of action | 4–6 hours[1] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| ChemSpider |
|
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C15H22N2 |
| Molar mass | 230.355 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 71 to 73 °C (160 to 163 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
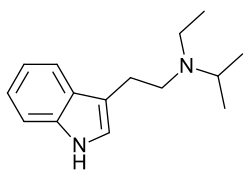
Ethylisopropyltryptamine (EiPT), also known as N-ethyl-N-isopropyltryptamine, is a psychedelic drug of the tryptamine family.[1] It is taken orally.[1]
EiPT appears to have been first synthesized and described by Alexander Shulgin.[1]
Use and effects
In his book TiHKAL (Tryptamines I Have Known and Loved), Alexander Shulgin lists the dose of EiPT as 24 to 40 mg and its duration as 4 to 6 hours.[1] According to Shulgin, this compound tends to produce nausea, dysphoria, and other unpleasant side effects.[1] It also seems to largely lack the hallucinatory and visual properties usually associated with psychedelic drugs.[1]
Interactions
Chemistry
EiPT is short for N-ethyl-N-isopropyltryptamine.[1] The full chemical name of this structure is N-ethyl-N-[2-(1H-indol-3-yl)ethyl]propan-2-amine. The compound is a substituted tryptamine, which all belong to a larger family of compounds known as indolethylamines.[1]
Synthesis
The chemical synthesis of EiPT has been described.[1]
Analogues
Analogues of EiPT include 4-HO-EiPT, 5-MeO-EiPT, methylisopropyltryptamine (MiPT), propylisopropyltryptamine (PiPT), ethylpropyltryptamine (EPT), diethyltryptamine (DET), and diisopropyltryptamine (DiPT), among others.[1]
Society and culture
Legal status
United States
EiPT is unscheduled and uncontrolled in the United States, but possession and sales of EiPT could be prosecuted under the Federal Analog Act because of its structural similarities to DET.
See also
References
External links
| Tryptamines |
|
|---|---|
| 4-Hydroxytryptamines and esters/ethers |
|
| 5-Hydroxy- and 5-methoxytryptamines |
|
| N-Acetyltryptamines |
|
| α-Alkyltryptamines |
|
| Cyclized tryptamines |
|
| Isotryptamines | |
| Related compounds |
|
| |