TOM (psychedelic)
TOM, or methylthio-methyl-methoxyamphetamine, is a series of lesser-known psychedelic drugs and substituted amphetamines with the molecular formula C12H19NOS. 2-TOM and 5-TOM are the 2- and 5-methylthio analogs of 2,5-dimethoxy-4-methylamphetamine (DOM), respectively. They were first synthesized by Alexander Shulgin and described in his book PiHKAL.[1][2] Very little is known about their dangers or toxicity.
2-TOM
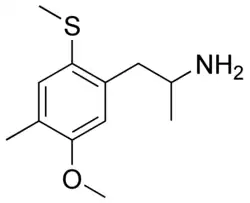
- Dosage: 60–100 mg
- Duration: 8–10 hours
- Effects: strong closed-eye visuals upon listening to music
5-TOM

- Dosage: 30–50 mg
- Duration: 6–10 hours
- Effects: open and closed-eye visuals, psychedelia, hallucinations
See also
References
| Phenethylamines |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Phentermines |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Cathinones |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Phenylisobutylamines (and further-extended) | |||||||||||||||||
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Cyclized phenethylamines |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Related compounds |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from WikiProjectMed. The text is available under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License unless otherwise noted. Additional terms may apply for the media files.