3C-MAL
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 4-Methylallyloxy-3,5-dimethoxyamphetamine; 3,5-Dimethoxy-4-methylallyloxyamphetamine; α-Methylmethallylescaline; α-Methyl-MAL; 3C-Methallylescaline |
| Routes of administration | Unknown[1] |
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Duration of action | Unknown[1] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
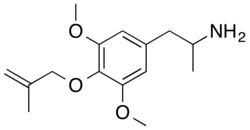
| Formula | C15H23NO3 |
| Molar mass | 265.353 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
| Melting point | 159 to 160 °C (318 to 320 °F) |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
3C-MAL, also known as 4-methylallyloxy-3,5-dimethoxyamphetamine or as α-methylmethallylescaline (3C-methallylescaline), is a chemical compound of the phenethylamine, amphetamine, and 3C families related to the psychedelic drug 3,4,5-trimethoxyamphetamine (TMA).[1][2] It is the amphetamine (3C) analogue of the psychedelic methallylescaline (MAL).[1][2] The compound does not appear to have been tested in humans, and its dose, duration, and effects are unknown.[1] Its chemical synthesis has been described.[2] 3C-MAL was first described in the scientific literature by Daniel Trachsel in 2002.[1][2]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 Trachsel D, Lehmann D, Enzensperger C (2013). Phenethylamine: von der Struktur zur Funktion [Phenethylamines: From Structure to Function]. Nachtschatten-Science (in German) (1 ed.). Solothurn: Nachtschatten-Verlag. p. 736. ISBN 978-3-03788-700-4. OCLC 858805226. Retrieved 31 January 2025.
- 1 2 3 4 Trachsel D (2002). "Synthesis of novel (phenylalkyl)amines for the investigation of structure-activity relationships. Part 1. Mescalin derivatives". Helvetica Chimica Acta. 85 (9): 3019–3026. doi:10.1002/1522-2675(200209)85:9<3019::AID-HLCA3019>3.0.CO;2-4.