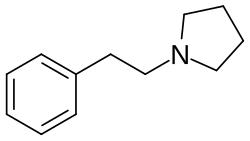
Phenylethylpyrrolidine
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
1-(2-Phenylethyl)pyrrolidine | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChemSpider | |
PubChem CID |
|
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C12H17N |
| Molar mass | 175.275 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
1-(2-Phenylethyl)pyrrolidine (PEP) is a chemical compound. It is an analogue of 2-phenylethylamine where the amine has been replaced by a pyrrolidine ring. The β-keto derivative is phenacylpyrrolidine and the α-methyl and β-keto (i.e., cathinone) derivative is α-pyrrolidinopropiophenone (α-PPP).
PEP is the base chemical structure for a series of stimulant drugs, including:
All of these compounds differ from PEP in that the alpha carbon is extended and a ketone is attached to the beta carbon (with the exception of prolintane), among other modifications.
See also
References
Chemical classes of psychoactive drugs | |
|---|---|
| Stimulants |
|
| Depressants |
|
| Entactogens | |
| Hallucinogens |
|
| Psychiatric drugs |
|
| Others |
|
This article is issued from WikiProjectMed. The text is available under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License unless otherwise noted. Additional terms may apply for the media files.