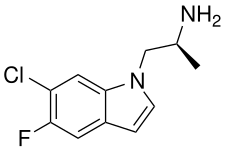
Ro60-0175
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Ro-60-0175; Ro-600175; Ro600175; RO-600175; (S)-5-Fluoro-6-chloro-α-methylisotryptamine; (S)-5-F-6-Cl-isoAMT |
| Drug class | Serotonin 5-HT2 receptor agonist |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| IUPHAR/BPS | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.189.524 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C11H12ClFN2 |
| Molar mass | 226.68 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Ro60-0175, or Ro-600175, also known as (S)-5-fluoro-6-chloro-α-methylisotryptamine ((S)-5-F-6-Cl-isoAMT), is a serotonin 5-HT2 receptor agonist of the isotryptamine family developed by Hoffmann–La Roche, which has applications in scientific research.[1][2][3] It is the enantiopure (S)- isomer of the 5-fluoro and 6-chloro derivative of α-methylisotryptamine (isoAMT).[1]
It acts as a potent and selective agonist of both the serotonin 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptor subtypes, with good selectivity over the closely related serotonin 5-HT2A subtype, and little or no affinity at other receptors.[4][5] However, Ro60-0175 also activates the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor less potently than the serotonin 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors.[6] Its EC50 and Emax values have been found to be 0.91–2.4 nM (79–130%) at the serotonin 5-HT2B receptor, 32–52 nM (84–88%) at the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor, and 400–447 nM (69–91%) at the serotonin 5-HT2A receptor.[1]
The drug has been found to produce hypolocomotion and sedative-like effects,[7] antidepressant-like effects,[8] anxiolytic-like effects[9] or no change in anxiety-like responses,[7][10] anti-obsessive-like effects,[10] antipsychotic-like effects,[10] appetite suppression,[11] and penile erections in rodent animal studies.[12] It fully generalizes with the preferential serotonin 5-HT2C receptor agonist meta-chlorophenylpiperazine (mCPP) in rodent drug discrimination tests, which can be blocked by the selective serotonin 5-HT2C receptor antagonist SB-242084.[13] Ro60-0175 also generalizes with the selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor (SSRI) citalopram in rodent drug discrimination tests, which can likewise be blocked by SB-242084, suggesting a major role for the serotonin 5-HT2C receptor in the interoceptive effects of SSRIs.[14] The drug has been found to inhibit dopaminergic signaling in the mesolimbic pathway.[15][16]
Ro60-0175 does not induce the head-twitch response, a behavioral proxy of psychedelic effects, when administered alone in rodents.[17][6] In addition, it suppresses the head-twitch response induced by the psychedelic drug (R)-DOI.[18][19] However, in combination with the selective serotonin 5-HT2C receptor antagonist SB-242084, Ro60-0175 robustly induces the head-twitch response.[17][6] This effect is abolished by addition of the selective serotonin 5-HT2A receptor antagonist ketanserin or volinanserin.[6] The preceding findings suggest that Ro60-0175 may be a serotonergic psychedelic and may have hallucinogenic effects in humans at sufficiently high doses or in combination with a serotonin 5-HT2C receptor antagonist.[6]
The drug was first described in the scientific literature by 1996.[8] It was under development by Roche for the treatment of major depressive disorder (MDD), anxiety disorders, and obsessive–compulsive disorder (OCD), and reached the preclinical research stage of development, but development was discontinued in 1997.[20][21]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 Shimada I, Maeno K, Kazuta K, Kubota H, Kimizuka T, Kimura Y, et al. (February 2008). "Synthesis and structure-activity relationships of a series of substituted 2-(1H-furo[2,3-g]indazol-1-yl)ethylamine derivatives as 5-HT2C receptor agonists". Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry. 16 (4): 1966–1982. doi:10.1016/j.bmc.2007.10.100. PMID 18035544.
- ↑ Quarta D, Naylor CG, Stolerman IP (August 2007). "The serotonin 2C receptor agonist Ro-60-0175 attenuates effects of nicotine in the five-choice serial reaction time task and in drug discrimination". Psychopharmacology. 193 (3): 391–402. doi:10.1007/s00213-007-0802-3. PMID 17473916. S2CID 21020653.
- ↑ Fletcher PJ, Rizos Z, Sinyard J, Tampakeras M, Higgins GA (May 2008). "The 5-HT2C receptor agonist Ro60-0175 reduces cocaine self-administration and reinstatement induced by the stressor yohimbine, and contextual cues". Neuropsychopharmacology. 33 (6): 1402–1412. doi:10.1038/sj.npp.1301509. PMID 17653111.
- ↑ Porter RH, Benwell KR, Lamb H, Malcolm CS, Allen NH, Revell DF, et al. (September 1999). "Functional characterization of agonists at recombinant human 5-HT2A, 5-HT2B and 5-HT2C receptors in CHO-K1 cells". British Journal of Pharmacology. 128 (1): 13–20. doi:10.1038/sj.bjp.0702751. PMC 1571597. PMID 10498829.
- ↑ Damjanoska KJ, Muma NA, Zhang Y, D'Souza DN, Garcia F, Carrasco GA, et al. (March 2003). "Neuroendocrine evidence that (S)-2-(chloro-5-fluoro-indol- l-yl)-1-methylethylamine fumarate (Ro 60-0175) is not a selective 5-hydroxytryptamine(2C) receptor agonist". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 304 (3): 1209–1216. doi:10.1124/jpet.102.043489. PMID 12604698. S2CID 23880629.
- 1 2 3 4 5 Vickers SP, Easton N, Malcolm CS, Allen NH, Porter RH, Bickerdike MJ, et al. (2001). "Modulation of 5-HT(2A) receptor-mediated head-twitch behaviour in the rat by 5-HT(2C) receptor agonists". Pharmacology, Biochemistry, and Behavior. 69 (3–4): 643–652. doi:10.1016/s0091-3057(01)00552-4. PMID 11509227.
- 1 2 Kennett G, Lightowler S, Trail B, Bright F, Bromidge S (January 2000). "Effects of RO 60 0175, a 5-HT(2C) receptor agonist, in three animal models of anxiety". European Journal of Pharmacology. 387 (2): 197–204. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(99)00706-2. PMID 10650160.
- 1 2 Moreau JL, Bös M, Jenck F, Martin JR, Mortas P, Wichmann J (August 1996). "5HT2C receptor agonists exhibit antidepressant-like properties in the anhedonia model of depression in rats". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 6 (3): 169–175. doi:10.1016/0924-977x(96)00015-6. PMID 8880075.
- ↑ Jenck F, Moreau JL, Berendsen HH, Boes M, Broekkamp CL, Martin JR, et al. (August 1998). "Antiaversive effects of 5HT2C receptor agonists and fluoxetine in a model of panic-like anxiety in rats". European Neuropsychopharmacology. 8 (3): 161–168. doi:10.1016/s0924-977x(97)00055-2. PMID 9716307.
- 1 2 3 Bishop MJ, Nilsson BM (2003). "New 5-HT2C receptor agonists". Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents. 13 (11): 1691–1705. doi:10.1517/13543776.13.11.1691. ISSN 1354-3776. Retrieved 12 October 2025.
- ↑ Clifton PG, Lee MD, Dourish CT (October 2000). "Similarities in the action of Ro 60-0175, a 5-HT2C receptor agonist and d-fenfluramine on feeding patterns in the rat". Psychopharmacology. 152 (3): 256–267. doi:10.1007/s002130000504. PMID 11105935.
- ↑ Millan MJ, Peglion JL, Lavielle G, Perrin-Monneyron S (April 1997). "5-HT2C receptors mediate penile erections in rats: actions of novel and selective agonists and antagonists". European Journal of Pharmacology. 325 (1): 9–12. doi:10.1016/s0014-2999(97)89962-1. PMID 9151932.
- ↑ Dekeyne A, Girardon S, Millan MJ (March 1999). "Discriminative stimulus properties of the novel serotonin (5-HT)2C receptor agonist, RO 60-0175: a pharmacological analysis". Neuropharmacology. 38 (3): 415–423. doi:10.1016/s0028-3908(98)00203-2. PMID 10219979.
- ↑ Millan MJ, Girardon S, Dekeyne A (March 1999). "5-HT2C receptors are involved in the discriminative stimulus effects of citalopram in rats". Psychopharmacology. 142 (4): 432–434. doi:10.1007/s002130050910. PMID 10229070.
- ↑ Di Matteo V, Di Giovanni G, Di Mascio M, Esposito E (August 1999). "SB 242084, a selective serotonin2C receptor antagonist, increases dopaminergic transmission in the mesolimbic system". Neuropharmacology. 38 (8): 1195–1205. doi:10.1016/s0028-3908(99)00047-7. PMID 10462132.
- ↑ Di Matteo V, Di Giovanni G, Di Mascio M, Esposito E (May 2000). "Biochemical and electrophysiological evidence that RO 60-0175 inhibits mesolimbic dopaminergic function through serotonin(2C) receptors". Brain Research. 865 (1): 85–90. doi:10.1016/s0006-8993(00)02246-0. PMID 10814735.
- 1 2 Nilsson BM (July 2006). "5-Hydroxytryptamine 2C (5-HT2C) receptor agonists as potential antiobesity agents". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 49 (14): 4023–4034. doi:10.1021/jm058240i. PMID 16821762.
- ↑ Canal CE, Booth RG, Morgan D (July 2013). "Support for 5-HT2C receptor functional selectivity in vivo utilizing structurally diverse, selective 5-HT2C receptor ligands and the 2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine elicited head-twitch response model". Neuropharmacology. 70: 112–121. doi:10.1016/j.neuropharm.2013.01.007. PMC 3754837. PMID 23353901.
- ↑ Fantegrossi WE, Simoneau J, Cohen MS, Zimmerman SM, Henson CM, Rice KC, et al. (December 2010). "Interaction of 5-HT2A and 5-HT2C receptors in R(-)-2,5-dimethoxy-4-iodoamphetamine-elicited head twitch behavior in mice". The Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics. 335 (3): 728–734. doi:10.1124/jpet.110.172247. PMC 2993545. PMID 20858706.
- ↑ "RO 600175". AdisInsight. 21 March 2000. Retrieved 14 October 2025.
- ↑ "Delving into the Latest Updates on RO-600175 with Synapse". Synapse. 4 October 2025. Retrieved 14 October 2025.