Homarylamine
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | 1,3-benzodioxolyl-N-methyl-5-ethanamine; 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methyl-2-phenylethylamine; Norlobivine |
| Routes of administration | Various |
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| ChEMBL | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
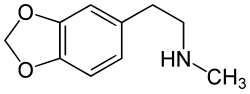
| Formula | C10H13NO2 |
| Molar mass | 179.219 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Homarylamine (INN;[1] also known as 3,4-methylenedioxy-N-methylphenethylamine and MDMPEA) is an antitussive (anti-cough) drug[2] which was patented in 1956 by Merck & Co.,[3] but has never been used medically as such.
Chemically it is a substituted phenethylamine. It is the N-methylated analog of methylenedioxyphenethylamine (MDPEA). It is a schedule I drug in the USA as a positional isomer of MDA.
Reactions
Reaction of homoarylamine with formaldehyde gives hydrastinine.
A practical application of homarylamine is in the synthesis of Roemerin.[4]
See also
- Lobivine (MDDMPEA)
- Hydrastine, an alkaloid derivative of homarylamine
References
- ↑ "International Non-Proprietary Names for Pharmaceutical Preparations" (PDF). Chronicle of the World Health Organization. 12 (3). 1958.
- ↑ Stefko PL, Denzel J, Hickey I (March 1961). "Experimental Investigation of Nine Antitussive Drugs". Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 50 (3): 216–221. Bibcode:1961JPhmS..50..216S. doi:10.1002/jps.2600500309.
- ↑ U.S. patent 2,820,739
- ↑ Marion, L., Grassie, V. (August 1944). "The Synthesis of l-Roemerine 1". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 66 (8): 1290–1292. Bibcode:1944JAChS..66.1290M. doi:10.1021/ja01236a024.
| DRAsTooltip Dopamine releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NRAsTooltip Norepinephrine releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| SRAsTooltip Serotonin releasing agents |
| ||||||||||||||
| Others |
| ||||||||||||||
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Monoamine reuptake inhibitors • Adrenergics • Dopaminergics • Serotonergics • Monoamine metabolism modulators • Monoamine neurotoxins | |||||||||||||||
| Phenethylamines |
| ||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amphetamines |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Phentermines |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Cathinones |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Phenylisobutylamines (and further-extended) | |||||||||||||||||
| Catecholamines (and close relatives) |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Cyclized phenethylamines |
| ||||||||||||||||
| Related compounds |
| ||||||||||||||||
| |||||||||||||||||
This article is issued from WikiProjectMed. The text is available under Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike License unless otherwise noted. Additional terms may apply for the media files.