Lys-MDMA
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Lysine-MDMA; N-(L-Lysinamidyl)-3,4-methylenedioxymethamphetamine; N-(L-Lysinamidyl)-MDMA; lysMDMA |
| Drug class | Inactive[1] |
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
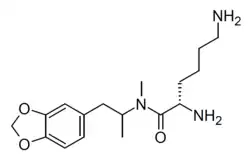
| Formula | C17H27N3O3 |
| Molar mass | 321.421 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Lys-MDMA, or lysine-MDMA, also known as N-(L-lysinamidyl)-MDMA, is an intended prodrug of MDMA which was being investigated for possible use as a pharmaceutical drug in the treatment of psychiatric disorders.[2][3][4][5][6] Structurally, lys-MDMA is to MDMA as lisdexamfetamine is to dextroamphetamine[5][4] As of August 2024, a phase 1 clinical trial comparing MDMA, MDA, lys-MDMA, and lys-MDA has been conducted and completed.[2][3][6] Lys-MDMA was being developed by MindMed.[3][6]
The published phase 1 clinical trial unexpectedly found that lys-MDMA does not convert into MDMA in humans and is completely inactive.[1] This is in contrast to lisdexamfetamine and lys-MDA, where are converted into dextroamphetamine and MDA, respectively.[1] The lack of conversion was attributed to steric hindrance caused by the N-methyl group of lys-MDMA.[1]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 Straumann I, Vizeli P, Avedisian I, Erne L, Noorshams D, Vukalovic I, Eckert A, Luethi D, Rudin D, Liechti ME (September 2025). "Acute effects of MDMA, MDA, lysine-MDMA, and lysine-MDA in a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, crossover trial in healthy participants". Neuropsychopharmacology. doi:10.1038/s41386-025-02248-3. PMID 40999236.
- 1 2 Elliott SP, Holdbrook T, Brandt SD (May 2020). "Prodrugs of New Psychoactive Substances (NPS): A New Challenge" (PDF). Journal of Forensic Sciences. 65 (3): 913–920. doi:10.1111/1556-4029.14268. PMID 31943218.
Lisdexamfetamine (N-(1-phenylpropan-2-yl)lysinamide) (Fig. 1A) can be prescribed in the treatment of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in children and binge eating disorder in adults and consists of dextroamphetamine (d-amphetamine) derivatized with the amino acid L-lysine (11,12). While lisdexamphetamine itself is pharmacologically inactive, in vivo peptidase enzymes associated with red blood cells hydrolyze the amide bond, thereby allowing pharmacological effects being exerted through d-amphetamine (13). The delayed absorption and metabolic profile for formation of the active drug reduces lisdexamfetamine's abuse liability and increases its safety profile (11,12). However, use of lisdexamfetamine has been mentioned in some Internet user forums as well as lysineMDMA (5,14,15).
- 1 2 3 Clinical trial number NCT04847206 for "Effects of MDMA-like Substances in Healthy Subjects (MDMA-like)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- 1 2 US 11896670, Trachsel D, Liechti ME, Lustenberger F, "Synthesis routes to access MDMA prodrugs by using controlled and non-controlled intermediates", issued 13 February 2024, assigned to Mind Medicine Inc.
- 1 2 "(2S)-2,6-diamino-N-[1-(1,3-benzodioxol-5-yl)propan-2-yl]-N-methylhexanamide". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine. Retrieved 13 November 2024.
- 1 2 3 Mind Medicine (MindMed) (20 September 2022). "MindMed Collaborators Dose First Patient in Phase 1 Investigator-Initiated Trial of MDMA-Like Substances". PR Newswire. Retrieved 13 November 2024.