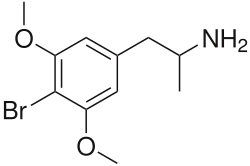
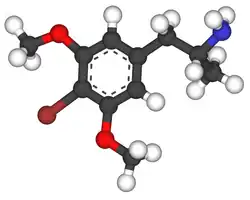
Cyclized
phenethylamines | | Phenylalkylpyrrolidines | |
|---|
2-Benzylpiperidines
(phenidates) | |
|---|
Phenylmorpholines
(phenmetrazines) | |
|---|
Phenyloxazolamines
(aminorexes) | |
|---|
Isoquinolines and
tetrahydroisoquinolines | |
|---|
| 2-Aminoindanes | |
|---|
| 2-Aminotetralins | |
|---|
| Others / unsorted |
- 1-Aminomethylindanes (e.g., 2CB-Ind, AMMI, bromojimscaline, jimscaline)
- 2-ADN
- 2-Benzhydrylpyrrolidine
- 2C-B-5-hemiFLY-α6 (BNAP)
- 2C-B-PYR
- 2CBecca
- 2CJP
- 2CLisaB
- 2CLisaH
- 3-Benzazepines (e.g., fenoldopam, lorcaserin, 7-chlorolorcaserin, SCHEMBL5334361)
- 3-Benzhydrylmorpholine
- 3-Phenylpiperidines (e.g., 3-phenylpiperidine, 3-PPP, OSU-6162 (PNU-96391), LPH-5, LPH-48, Z3517967757 (Z7757))
- 6-AB
- AL-1095
- Aminochromes (e.g., adrenochrome, adrenolutin)
- Benzocyclobutenes (e.g., 2CBCB-NBOMe, bromotomscaline, S33005, TCB-2, tomscaline)
- Benzoxepins (e.g., BBOX, IBOX, TFMBOX)
- Butyltolylquinuclidine
- Camfetamine
- Cypenamine (trans-2-phenylcyclopentylamine)
- Diphenidine
- Diphenylprolinol
- DMBMPP
- Ergolines (e.g., LSD)
- Fencamfamin
- GYKI-52895
- HDMP-29
- Ivabradine
- Methoxphenidine
- Methylmorphenate
- Milnacipran
- MT-45
- 2-Naphthylamine
- Org 6582
- Partial ergolines (e.g., NDTDI, RU-27849, DEIMDHPCA, DEMPDHPCA, DEMPDHPCA-2C-D, RU-27251)
- PF-592,379
- Phenylcyclopropylamines (e.g., DMCPA, TMT, tranylcypromine)
- Phenylpiracetams (e.g., phenylpiracetam, MRZ-9547, RGPU-95)
- Pyridopyrroloquinoxalines (e.g., lumateperone, deulumateperone, IHCH-7079, IHCH-7086, IHCH-7113, ITI-1549)
- Tetrahydrobenzopyranylamines (e.g., CT-5126)
- Tolazoline
- Tricyclics (e.g., AMDA, AMDH, benzoctamine, dizocilpine, SpAMDA)
- ZC-B
|
|---|
|
|---|
| Related compounds |
- 2-Furylethylamine
- 2-Pyrrolylethylamine
- 3-Pyrrolylethylamine
- 3-Pyrrolylpropylamine
- 2-Tetrahydrofurylethylamine
- 4-Benzylpiperidine
- 7-AB
- Alkylamines (e.g., 1,3-DMBATooltip 1,3-dimethylbutylamine, 1,4-DMAATooltip 1,4-dimethylamylamine, heptaminol, iproheptine, isometheptene, methylhexanamine/1,3-DMAA, octodrine, oenethyl, tuaminoheptane)
- Benzylamines (e.g., benzylamine, α-methylbenzylamine, MDM1EA, ALPHA, M-ALPHA, pargyline)
- Benzylpiperazines (e.g., benzylpiperazine, MDBZP, fipexide)
- Cyclohexylaminopropanes (e.g., propylhexedrine, norpropylhexedrine)
- Cyclopentylaminopropanes (e.g., isocyclamine, cyclopentamine)
- Phenoxyethylamines (e.g., 3,4,5-trimethoxyphenoxyethylamine, CT-4719, ORG-37684)
- Phenylalkenylamines (e.g., phenylbutenamine)
- Phenylalkynylamines (e.g., phenylbutynamine)
- Phenylpiperazines (e.g., 1-phenylpiperazine, mCPPTooltip meta-chlorophenylpiperazine, TFMPPTooltip trifluoromethylphenylpiperazine, oMPPTooltip ortho-methylphenylpiperazine, pFPPTooltip para-fluorophenylpiperazine, pMeOPPTooltip para-methoxyphenylpiperazine)
- Phenylpropylamines (e.g., phenylpropylamine, homo-MDA, homo-MDMA)
- Thienylaminopropanes (thiopropamines) (e.g., thiopropamine, methiopropamine, thiothinone)
|
|---|