Renanolone
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| ATC code |
|
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
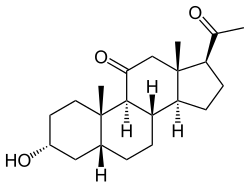
| Formula | C21H32O3 |
| Molar mass | 332.484 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Renanolone (INN; also known as 11-ketopregnanolone or 5β-pregnan-3α-ol-11,20-dione) is a synthetic neuroactive steroid which is described as a general anesthetic, but was never introduced for clinical use.[1] Its isomers, alfaxolone and alfadolone, are also general anesthetics, and are known to act as positive allosteric modulators of the GABAA receptor, a property which is likely the case for renanolone as well.
Chemistry
See also
References
- ↑ Hill RA, Makin HL, Kirk DN, Murphy GM (23 May 1991). Dictionary of Steroids. CRC Press. p. 592. ISBN 978-0-412-27060-4.