Liver abscess
| Liver abscess | |
|---|---|
| Other names: Hepatic abscess[1] | |
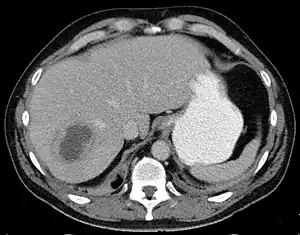 | |
| Liver abscess on axial CT image: a hypodense lesion in the liver with peripherally enhancement. | |
| Specialty | General surgery, Infectious disease |
A liver abscess is a mass filled with pus inside the liver.[2] Common causes are abdominal conditions such as appendicitis or diverticulitis due to haematogenous spread through the portal vein.[3] It can also develop as a complication of a liver injury.
Types
There are several major forms of liver abscess, classified by cause:
- Pyogenic liver abscess, which is most often polymicrobial, accounts for 80% of hepatic abscess cases in the United States.
- Amoebic liver abscess due to Entamoeba histolytica accounts for 10% of cases. The incidence is much higher in developing countries.
- Fungal abscess, most often due to Candida species, accounts for less than 10% of cases.
- Iatrogenic abscess, caused by medical interventions
Signs and symptoms
The clinical presentation for a liver abscess is consistent with:[4]
- Fever
- Night sweats
- Malaise
- Vomiting
Causes
Risk factors for developing liver abscess can be due to infection, post-procedural infection and metastasis such as primary liver tumours, liver metastasis, biliary procedures, biliary injuries, biliary tract disease, appendicitis, and diverticulitis.
Major bacterial causes of liver abscess include the following:[5]
- Streptococcus species (including Enterococcus)
- Escherichia species
- Staphylococcus species
- Klebsiella species (Higher rates in the Far East)
- Anaerobes (including Bacteroides species)
- Pseudomonas species
- Proteus species
- Entamoeba Histolytica
However, as noted above, many cases are polymicrobial.
Diagnosis
In terms of the evaluation of liver abscess in the affected individual are the following are done:[6]
- CBC
- Ultrasound
- CT scan
-
.png) a) Fluoroscopic view shows contrast in collapsed liver abscess red arrow b) fluoroscopic view shows contrast tracking from the liver abscess red arrow
a) Fluoroscopic view shows contrast in collapsed liver abscess red arrow b) fluoroscopic view shows contrast tracking from the liver abscess red arrow -
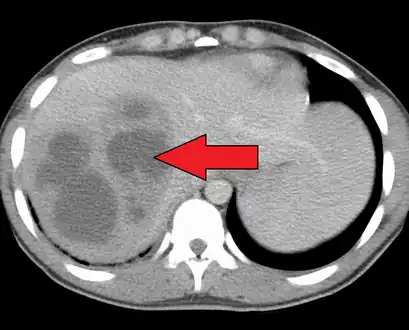 A large pyogenic liver abscess presumed to be the result of appendicitis
A large pyogenic liver abscess presumed to be the result of appendicitis
Differential diagnosis
As to the DDx in an individual with a liver abscess we look at:[4][7]
- Right lower lobe pneumonia
- Necrotic liver masses
Management
Antibiotics: IV metronidazole and third generation cephalosporin/quinolones, β-lactam antibiotics, and aminoglycosides are effective.
Prognosis
The prognosis has improved for liver abscesses. The mortality rate in-hospital is about 2.5-19%. The elderly, ICU admissions, shock, cancer, fungal infections, cirrhosis, chronic kidney disease, acute respiratory failure, severe disease, or disease of biliary origin have a worse prognosis.[4]
References
- ↑ "Hepatic Abscess | Johns Hopkins ABX Guide". www.hopkinsguides.com. Archived from the original on 2023-06-02. Retrieved 2025-07-22.
- ↑ "Liver Abscess Definition in Medical Conditions Dictionary". medconditions.net. 11 April 2018. Archived from the original on 5 April 2012. Retrieved 11 April 2018.
- ↑ MedlinePlus Encyclopedia: Pyogenic liver abscess
- ↑ 4.0 4.1 4.2 Akhondi H, Sabih DE (2019). "Liver Abscess". StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. PMID 30855818. Archived from the original on 2021-05-03. Retrieved 2019-07-28.
- ↑ Webb GJ, Chapman TP, Cadman PJ, Gorard DA (January 2014). "Pyogenic liver abscess". Frontline Gastroenterology. 5 (1): 60–67. doi:10.1136/flgastro-2013-100371. PMC 5369710. PMID 28839753.
- ↑ "Liver Abscess Workup: Laboratory Studies, Imaging Studies, Percutaneous Aspiration and Drainage". emedicine.medscape.com. Archived from the original on 17 May 2024. Retrieved 22 July 2025.
- ↑ "Liver Abscess Differential Diagnoses". emedicine.medscape.com. Archived from the original on 17 May 2024. Retrieved 7 August 2025.
External links
| Classification | |
|---|---|
| External resources |
- Liver Abscess CT Images Archived 2016-03-04 at the Wayback Machine CTCases Liver Abscess CT Scan.