Indometacin farnesil
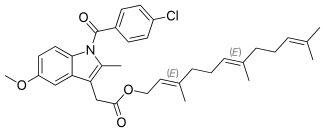 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | International Drug Names |
| Routes of administration | Oral |
| ATC code |
|
| Legal status | |
| Legal status |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Metabolism | To indometacin |
| Elimination half-life | 1.5 hours |
| Excretion | Renal |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.242.585 |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C34H40ClNO4 |
| Molar mass | 562.15 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
| (verify) | |
Indometacin farnesil (INN) is a prodrug of the nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug (NSAID) indometacin,[1] designed to reduce the occurrence of side-effects by esterification of the carboxyl group on indometacin with farnesol. Indometacin farnesil was first approved in Japan in 1991, and is available in Japan[2] and Indonesia, under the trade names Infree and Dialon, respectively.
References
- ↑ Hirohata S, Yanagida T, Kawai M, Kikuchi H (November 1999). "Inhibition of human B cell activation by a novel nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug, indometacin famesil". Immunopharmacology. 44 (3): 245–254. doi:10.1016/S0162-3109(99)00084-3. PMID 10598881.
- ↑ "Infree (indometacin farnesil capsules) Full Prescribing Information" (PDF). Eisai Co., Ltd. Archived from the original (PDF) on 2010-12-03. from Eisai Co.