Dolichocolon
| Dolichocolon | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Redundant colon, tortuous colon, floppy colon |
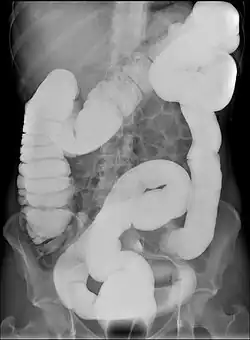 | |
| Abdominal X-ray image with bowel contrast agent showing dolichocolon | |
| Specialty | Gastroenterology, colorectal surgery, general surgery |
| Complications | Volvulus, Chilaiditi syndrome |
| Usual onset | From birth |
| Duration | Indefinite |
| Causes | Unknown |
| Diagnostic method | Abdominal X-ray, colonoscopy |
| Differential diagnosis | Megacolon |
| Prognosis | Most commonly asymptomatic |
Dolichocolon, also known as redundant colon or tortuous colon, is the congenital presence of an abnormally-long large intestine.[1] It should not be confused with an abnormally wide large intestine, which is called megacolon. The name originates from Ancient Greek: δολιχός, romanized: dolĭkhós, lit. 'long, protracted', and "colon".
Dolichocolon may predispose to abnormal rotation of the colon (volvulus) and its interposition between the diaphragm and the liver (Chilaiditi syndrome). The exact cause remains unknown.[2] Dolichocolon is often an incidental finding on abdominal X-rays or in colonoscopy. It is not by itself a disease and as such requires no treatment if asymptomatic.
References
- ↑ Vadera, Sonam; Knipe, Henry; Niknejad, Mohammad Taghi; Bell, Daniel J.; Sharma, Rohit; Gaillard, Frank (18 November 2023) [First published 12 October 2021]. "Dolichocolon". Radiopaedia (Reference article) (9th revision ed.). doi:10.53347/rID-93956. Archived from the original on 2024-06-15.
- ↑ Geng, Caitlin (19 December 2023) [First published 5 August 2022]. "Redundant colon: Signs, causes, and treatment". In Warner, Daisy; Sullivan, James (eds.). Medical News Today. Reviewed by Darragh O'Carroll, MD; Saurabh Sethi, MD, MPH. Healthline Media. Archived from the original on 2025-04-20.