Cevimeline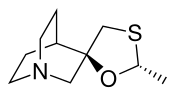 |
 |
|
| Pronunciation | se vim' e leen[1] |
|---|
| Trade names | Evoxac |
|---|
- (2R,2R)-2'-Methylspiro[4-azabicyclo[2.2.2]octane-2,5'-[1,3]oxathiolane]
|
|
| Drug class | Muscarinic agonist[1] |
|---|
| Main uses | Dry mouth[1] |
|---|
| Side effects | Increased sweating, runny nose, nausea, diarrhea, headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances, tiredness[1] |
|---|
Pregnancy
category | |
|---|
Routes of
use | By mouth (capsules) |
|---|
|
| AHFS/Drugs.com | Monograph |
|---|
| MedlinePlus | a608025 |
|---|
|
| Legal status |
- In general: ℞ (Prescription only)
|
|---|
|
| Protein binding | <20% |
|---|
|
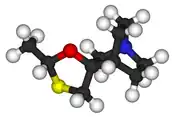
| Formula | C10H17NOS |
|---|
| Molar mass | 199.31 g·mol−1 |
|---|
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
|---|
O1[C@H](SC[C@@]12CN3CCC2CC3)C
|
InChI=1S/C10H17NOS/c1-8-12-10(7-13-8)6-11-4-2-9(10)3-5-11/h8-9H,2-7H2,1H3/t8-,10-/m1/s1  Y YKey:WUTYZMFRCNBCHQ-PSASIEDQSA-N  Y Y
|
Cevimeline, sold under the brand name Evoxac, is a medication used to treat dry mouth due to Sjögren's syndrome or radiation therapy.[1] It is similar to pilocarpine.[2] It is taken by mouth.[1]
Side effects are usually mild and may include increased sweating, runny nose, nausea, diarrhea, headaches, dizziness, visual disturbances, and tiredness.[1] Safety in pregnancy is unclear.[2] It is a muscarinic agonist, which results in increased saliva production.[1]
Cevimeline was approved for medical use in the United States in 2000.[2] It is available as a generic medication.[3] In the United States a month of medication costs about 52 USD as of 2021.[3]
Medical use
Dosage
The typical dose is 30 mg three times daily.[1]
Side effects
Known side effects include nausea, vomiting, diarrhea, excessive sweating, rash, headache, runny nose, cough, drowsiness, hot flashes, blurred vision, and difficulty sleeping.[4]
Contraindications include asthma and angle closure glaucoma.
Mechanism of action
By activating the M3 receptors of the parasympathetic nervous system, cevimeline stimulates secretion by the salivary glands, thereby alleviating dry mouth.
See also
- Pilocarpine — a similar parasympathomimetic medication for dry mouth (xerostomia)
- Bethanechol — a similar muscarinic parasympathomimetic with longer-lasting effect
References
External links
|
|---|
| mAChRs | | Agonists | |
|---|
| Antagonists |
- 3-Quinuclidinyl benzilate
- 4-DAMP
- Aclidinium bromide (+formoterol)
- Abediterol
- AF-DX 250
- AF-DX 384
- Ambutonium bromide
- Anisodamine
- Anisodine
- Antihistamines (first-generation) (e.g., brompheniramine, buclizine, captodiame, chlorphenamine (chlorpheniramine), cinnarizine, clemastine, cyproheptadine, dimenhydrinate, dimetindene, diphenhydramine, doxylamine, meclizine, mequitazine, perlapine, phenindamine, pheniramine, phenyltoloxamine, promethazine, propiomazine, triprolidine)
- AQ-RA 741
- Atropine
- Atropine methonitrate
- Atypical antipsychotics (e.g., clozapine, fluperlapine, olanzapine (+fluoxetine), rilapine, quetiapine, tenilapine, zotepine)
- Benactyzine
- Benzatropine (benztropine)
- Benzilone
- Benzilylcholine mustard
- Benzydamine
- BIBN 99
- Biperiden
- Bornaprine
- Camylofin
- CAR-226,086
- CAR-301,060
- CAR-302,196
- CAR-302,282
- CAR-302,368
- CAR-302,537
- CAR-302,668
- Caramiphen
- Cimetropium bromide
- Clidinium bromide
- Cloperastine
- CS-27349
- Cyclobenzaprine
- Cyclopentolate
- Darifenacin
- DAU-5884
- Desfesoterodine
- Dexetimide
- DIBD
- Dicycloverine (dicyclomine)
- Dihexyverine
- Difemerine
- Diphemanil metilsulfate
- Ditran
- Drofenine
- EA-3167
- EA-3443
- EA-3580
- EA-3834
- Emepronium bromide
- Etanautine
- Etybenzatropine (ethybenztropine)
- Fenpiverinium
- Fentonium bromide
- Fesoterodine
- Flavoxate
- Glycopyrronium bromide (+beclometasone/formoterol, +indacaterol)
- Hexahydrodifenidol
- Hexahydrosiladifenidol
- Hexbutinol
- Hexocyclium
- Himbacine
- HL-031,120
- Homatropine
- Imidafenacin
- Ipratropium bromide (+salbutamol)
- Isopropamide
- J-104,129
- Hyoscyamine
- Mamba toxin 3
- Mamba toxin 7
- Mazaticol
- Mebeverine
- Meladrazine
- Mepenzolate
- Methantheline
- Methoctramine
- Methylatropine
- Methylhomatropine
- Methylscopolamine
- Metixene
- Muscarinic toxin 7
- N-Ethyl-3-piperidyl benzilate
- N-Methyl-3-piperidyl benzilate
- Nefopam
- Octatropine methylbromide (anisotropine methylbromide)
- Orphenadrine
- Otenzepad (AF-DX 116)
- Otilonium bromide
- Oxapium iodide
- Oxitropium bromide
- Oxybutynin
- Oxyphencyclimine
- Oxyphenonium bromide
- PBID
- PD-102,807
- PD-0298029
- Penthienate
- Pethidine
- pFHHSiD
- Phenglutarimide
- Phenyltoloxamine
- Pipenzolate bromide
- Piperidolate
- Pirenzepine
- Piroheptine
- Pizotifen
- Poldine
- Pridinol
- Prifinium bromide
- Procyclidine
- Profenamine (ethopropazine)
- Propantheline bromide
- Propiverine
- Quinidine
- Revefenacin
- Rociverine
- RU-47,213
- SCH-57,790
- SCH-72,788
- SCH-217,443
- Scopolamine (hyoscine)
- Scopolamine butylbromide (hyoscine butylbromide)
- Silahexacyclium
- Sofpironium bromide
- Solifenacin
- SSRIs (e.g., femoxetine, paroxetine)
- Telenzepine
- Terodiline
- Tetracyclic antidepressants (e.g., amoxapine, maprotiline, mianserin, mirtazapine)
- Tiemonium iodide
- Timepidium bromide
- Tiotropium bromide
- Tiquizium bromide
- Tofenacin
- Tolterodine
- Tricyclic antidepressants (e.g., amitriptyline (+perphenazine), amitriptylinoxide, butriptyline, cidoxepin, clomipramine, desipramine, desmethyldesipramine, dibenzepin, dosulepin (dothiepin), doxepin, imipramine, lofepramine, nitroxazepine, northiaden (desmethyldosulepin), nortriptyline, protriptyline, quinupramine, trimipramine)
- Tridihexethyl
- Trihexyphenidyl
- Trimebutine
- Tripitamine (tripitramine)
- Tropacine
- Tropatepine
- Tropicamide
- Trospium chloride
- Typical antipsychotics (e.g., chlorpromazine, chlorprothixene, cyamemazine (cyamepromazine), loxapine, mesoridazine, thioridazine)
- Umeclidinium bromide (+vilanterol)
- WIN-2299
- Xanomeline
- Zamifenacin
|
|---|
|
|---|
Precursors
(and prodrugs) | |
|---|
See also: Receptor/signaling modulators • Nicotinic acetylcholine receptor modulators • Acetylcholine metabolism/transport modulators |

