Weismann-Netter–Stuhl syndrome
| Weismann-Netter–Stuhl syndrome | |
|---|---|
| Other names | Weismann-Netter syndrome, tibioperoneal diaphyseal toxopachyosteosis |
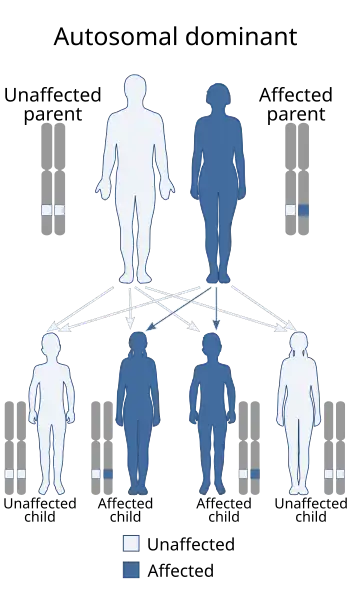 | |
| Weismann-Netter–Stuhl syndrome is inherited in an autosomal dominant manner. | |
Weismann-Netter–Stuhl syndrome, also known as Weismann-Netter syndrome or tibioperoneal diaphyseal toxopachyosteosis, is a rare disorder characterized by bowing of the lower legs and an abnormal thickening of thinner bone in the leg.[1]
The main sign is anterior bowing and posterior cortical thickening of the diaphyses of both the tibiae and fibulae. It is thought to be inherited in an autosomal dominant fashion and is most often bilateral and symmetric in nature. Associated features include dwarfism and mild intellectual disability as well as a process known as tibialization of the fibulae, which involves thickening and enlargement of these bones to an extent resembling the tibiae.[2] The combination of the presence of tibialization of the fibulae, which is highly specific for the disorder, and the absence of laboratory abnormalities, ruling out alternative diagnoses including rickets, essentially confirms the diagnosis.
Cause
This condition is unknown but currently thought to be genetic, with autosomal dominant inheritance.[3]
Diagnosis
Radiographic features
The most prominent and extensively documented findings of Weismann-Netter–Stuhl syndrome are on plain radiographs of the bones. Findings include bilateral and symmetric anterior bowing of both tibiae and fibulae, lateral bowing of the tibiae, femoral bowing, and squaring of iliac and pelvis bones.[4]
Management
Treatment for Weismann-Netter–Stuhl syndrome depends on the symptoms of the individual; many people with the condition do not report any. Management may include physical therapy, supportive social services, or, rarely, surgery.[3]
History
The features of this disorder were first described by French doctors Robert Weismann-Netter (1894–1980)[5] and L. Stuhl in their report first describing the association in seven patients in 1954.[6] They believed these seven patients had mistakenly been diagnosed as congenital syphilis or rickets, which remain considerations in the differential diagnosis of this syndrome today.[7]
References
- ↑ Gupta, P.; Mittal, R.; Mittal, S.; Shankar, V. (2014). "Weismann-Netter-Stuhl syndrome: report of two cases and treatment". Case Reports. 2014 (feb04 2): bcr2013201772. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-201772. ISSN 1757-790X. PMC 3918600. PMID 24496066.
- ↑ Robinow, M.; Johnson, G. F. (March 1988). "The Weismann-Netter syndrome". American Journal of Medical Genetics. 29 (3): 573–579. doi:10.1002/ajmg.1320290315. ISSN 0148-7299. PMID 3377000.
- 1 2 "Weismann-Netter-Stuhl Syndrome". National Organization for Rare Disorders. 2024-08-07. Retrieved 2025-09-03.
- ↑ Peippo, Maarit; Valanne, Leena; Perhomaa, Marja; Toivanen, Leena; Ignatius, Jaakko (November 2009). "Weismann-Netter syndrome and mental retardation: a new patient and review of the literature". American Journal of Medical Genetics. Part A. 149A (11): 2593–2601. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.33019. ISSN 1552-4833. PMID 19839038. S2CID 21805373.
- ↑ Beighton, Peter; Beighton, Greta (2012-12-06). The Man Behind the Syndrome. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 231. ISBN 978-1-4471-1415-4.
- ↑ Weismann-Netter, R.; Stuhl, L. (1954-11-24). "[Congenital osteopathy eventually familial defined especially by antero-posterior incurvation and thickening of both bones of the leg: diaphyseal tibio-peroneal toxopachyostosis]". La Presse Médicale. 62 (78): 1618–1622. ISSN 0032-7867. PMID 13237064.
- ↑ Gupta, Pratyush; Mittal, Ravi; Mittal, Samarth; Shankar, Vivek (2014-02-04). "Weismann-Netter-Stuhl syndrome: report of two cases and treatment". BMJ Case Reports. 2014: bcr2013201772. doi:10.1136/bcr-2013-201772. ISSN 1757-790X. PMC 3918600. PMID 24496066.