Vestibular duct
| Vestibular duct | |
|---|---|
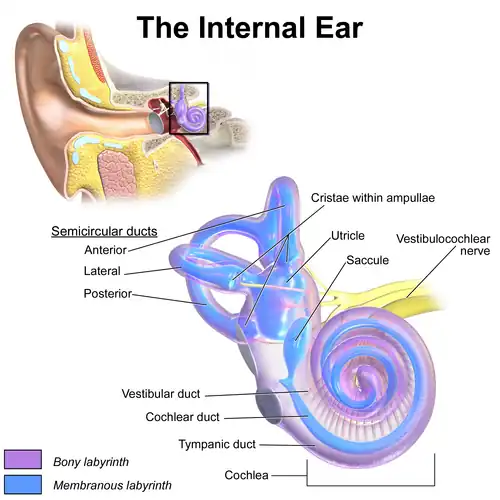 Inner ear, with vestibular duct labeled near bottom. | |
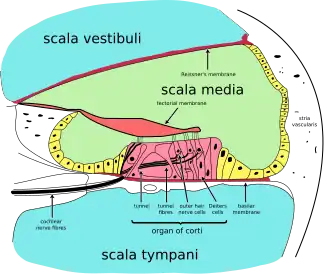 Cross section of the cochlea. | |
| Details | |
| Identifiers | |
| Latin | scala vestibuli |
| MeSH | D054738 |
| TA98 | A15.3.03.043 |
| TA2 | 6968 |
| FMA | 61269 |
| Anatomical terminology | |
The vestibular duct or scala vestibuli is a perilymph-filled cavity inside the cochlea of the inner ear that conducts sound vibrations to the cochlear duct.[1]
It is separated from the cochlear duct by Reissner's membrane and extends from the vestibule of the ear to the helicotrema where it joins the tympanic duct.
Additional images
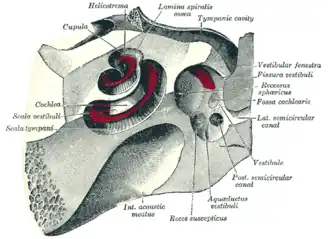 The cochlea and vestibule, viewed from above.
The cochlea and vestibule, viewed from above.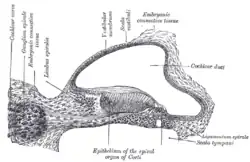 Transverse section of the cochlear duct of a fetal cat.
Transverse section of the cochlear duct of a fetal cat. Interior of right osseous labyrinth.
Interior of right osseous labyrinth.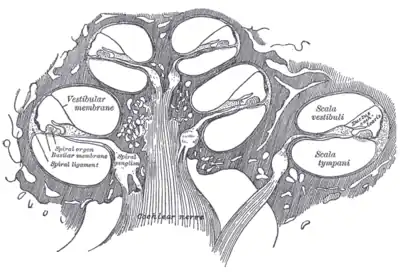 Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the cochlea.
Diagrammatic longitudinal section of the cochlea.
See also
References
- ↑ "Enlarged Vestibular Aqueducts (EVA) & Hearing Loss". National Institute of Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (NIDCD). 13 February 2017. Retrieved 6 November 2024.