Vaginal tumors are tumors found in the vagina.[1][2]
WHO 2020 classification
Tumors of the vagina[1]
|
|
Type |
Image
|
| Epithelial tumors of the vagina
|
Benign squamous lesions
|
Genital wart
|
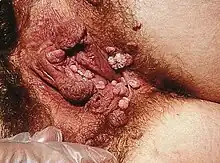
|
| Squamous papilloma
|
|
| Atrophy
|
|
| Tubulosquamous polyp
|
|
| Squamous cell tumors and precursors
|
Squamous intraepithelial lesion
|
|
| Squamous cell carcinoma, HPV-associated
|
|
| Squamous cell carcinoma, HPV-independent
|
|
| Squamous cell carcinoma NOS
|
|
| Benign glandular lesions
|
Villous adenoma
|
|
| Müllerian papilloma
|
|
| Vaginal adenosis
|
|
| Endocervicosis
|
|
| Cysts
|
|
| Glandular tumors
|
Adenocarcinoma, HPV-associated
|
|
| Endometrioid carcinoma
|
|
| Clear-cell carcinoma of the vagina
|
|
| Mucinous carcinoma, gastric type
|
|
| Mucinous carcinoma, intestinal type
|
|
| Mesonephric adenocarcinoma
|
|
| Carcinosarcoma
|
|
| Other epithelial tumors
|
Mixed tumor of the vagina
|
|
| Adenocarcinoma of Skene gland origin
|
|
| Adenosquamous carcinoma
|
|
| Adenoid basal carcinoma
|
|
| Mixed epithelial and msenchymal tumors
|
Adenosarcoma
|
|
|
| Miscellaneous tumors
|
Germ cell tumors
|
|
|
See also
References
External links
