Targeted protein degradation
Targeted protein degradation (TPD) is a drug design strategy that uses small molecules such as PROteolysis TArgeting Chimeras (PROTACs), molecular glues, or related approaches to induce the selective ubiquitination and subsequent proteasomal degradation of target proteins via the ubiquitin–proteasome system or other cellular clearance pathways.[1] Unlike traditional occupancy-driven inhibition, TPD agents catalytically trigger irreversible loss of disease-modifying proteins, enabling the removal of providing sustained duration of action after transient engagement of the target protein.[2] This event-driven approach is being investigated for potential therapeutic applications in oncology,[3] neurodegeneration,[4] and other areas.[5]
Mechanism
Small molecule drugs, compounds typically <1 kD in mass, comprise a large portion of the therapeutic market.[6] These drugs usually operate by agonizing or antagonizing the active site on a disease-linked protein of interest, though allosteric regulation is possible.[7] With an estimated 93% of the human proteome lacking druggable binding sites,[8] methods have been developed to modulate protein activity through binding of any available site rather than only the active site. These drugs contain a target protein binding warhead in addition to a linker-separated active domain. This domain may recruit a second protein to the proximity, induce protease-mediated degradation, or recruit a kinase for directed phosphorylation, among other functions.[9] These drugs expand both the mechanism of action for small molecule therapeutics and the pool of potential protein targets.[9]
Event-driven pharmacology
In the field of targeted protein degraders (TPDs), event-driven pharmacology describes a mechanism of action by which a drug exerts its biological effect not by maintaining continuous occupancy of its target, but rather by initiating an irreversible downstream event, such as the proteolytic degradation of the target protein. This contrasts with traditional occupancy-driven pharmacology, in which drug efficacy depends on sustained binding.[10][2]
TPDs act in a catalytic manner. Transient binding brings the target protein into proximity with an E3 ubiquitin ligase, resulting in its ubiquitination and subsequent degradation by the proteasome. Because the target protein is removed rather than merely inhibited, the pharmacological effect can persist after the TPD dissociates from the target or is cleared from the body, resulting prolonged duration of action at lower drug exposures.[10][2]
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras
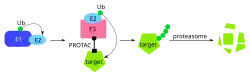
Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) were first reported by Kathleen Sakamoto, Craig Crews, and Raymond Deshaies in 2001. A chimeric molecule consisting of ovalicin (a MetAP-2 small molecule inhibitor) and IκBα phosphopeptide (a recruiter of the SCFβ-TRCP E3 ligase complex) separated by a linker was constructed and shown to induce MetAP-2 degradation in in vitro cell models. Further study confirmed that E3 ligase-mediated ubiquitination and subsequent proteasome degradation was responsible for reduced MetAP-2 levels.[11] Continued work on this system by Craig Crews and others has expanded the potential pool of E3 ligases and degradation targets with Arvinas Inc. founded in 2013 to bring PROTAC drugs to market.[12] As of April 2023, Arvinas has one drug in Stage 3 clinical trials (ARV-471, an estrogen receptor degrader), and two drugs in Stage 2 clinical trials (androgen receptor degraders ARV-110 and ARV-766) for treatment of breast and prostate cancer, respectively.[13] Arvinas released Phase 2 clinical trial results for ARV-471 in December, 2022.[14]
As of May 2025, PROTACs in active development that have reached at least Phase II clinical trials:[15]
| INN | Research code | Target | Indication | Developer | NCT number | Phase |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bavdegalutamide | ARV-110 | Androgen receptor | mCRPC (prostate cancer) | Arvinas | NCT03888612 [16] | I |
| Vepdegestrant | ARV-471 | Estrogen receptor | ER+ advanced/metastatic breast cancer | Arvinas / Pfizer | NCT05654623 [17] | III |
| Luxdegalutamide | ARV-766 | Androgen receptor | mCRPC (prostate cancer) | Arvinas | NCT05067140 [18] | II |
| BGB-16673 | BTK | B-cell malignancies (CLL, NHL, MCL) | BeiGene | NCT05006716 [19] | I/II | |
| Zelebrudomide | NX-2127 | BTK, IKZF1/IKZF3 | Relapsed/refractory B-cell malignancies | Nurix Therapeutics | NCT04830137 [20] | I/II |
| Bexobrutideg | NX-5948 | BTK | B-cell malignancies | Nurix Therapeutics | NCT05131022 [21] | I/II |
SNIPERs
SNIPERs (Specific and Non-genetic IAP-dependent Protein Erasers) are chimeric small molecules that hijack the E3 ligase activity of inhibitor of apoptosis proteins (IAPs), such as cIAP1 and XIAP, to selectively induce the ubiquitin-dependent proteasomal degradation of target proteins. SNIPERs are a subclass of PROTAC degraders that specifically use IAP family ligases. Notably, SNIPERs often also degrade the IAP ligases themselves along with the intended targets, which maybe beneficial in cancer cells that overexpress IAPs.[22][23]
Molecular glues
Molecular glues are small molecules that promote targeted protein degradation by stabilizing interactions between E3 ubiquitin ligases and target proteins, enabling their ubiquitin-proteasome mediated breakdown. Unlike bifunctional PROTACs, they lack a linker and directly enhance weak protein–protein interactions, leading to degradation of the target protein. Their small size enables high cell permeability and oral bioavailability. While early examples, such as thalidomide analogs recruiting cereblon, were discovered by accident, mechanistic and structural insights are now starting to drive their rational design.[24]
| Compound name | Target / Mechanism | Primary indication(s) | Most advanced phase | NCT number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Iberdomide (CC-220) | CRBN modulator, IKZF1/IKZF3 degrader | Multiple myeloma, lupus | Phase III | NCT04975997 [25] |
| Mezigdomide (CC-92480) | CRBN modulator, IKZF1/3 degrader | Relapsed / refractory multiple myeloma | Phase III | NCT05552976 [26] |
| Avadomide (CC-122) | CRBN modulator, IKZF1/3 degrader | NHL, DLBCL, solid tumors | Phase II | NCT03834623 [27] |
Hydrophobic tag degradation
Hydrophobic tag degraders contain a binding domain in addition to a linker-separated hydrophobic moiety, such as adamantyl, to induce protein degradation. An early example of a hydrophobically tagged degrader is fulvestrant, an estrogen receptor antagonist that contains a long hydrophobic side chain that induces the degradation of the estrogen receptor.[28][29][10] Fulvestrant has inspired the development of additional selective estrogen receptor degraders (SERDs).[30]
As exposed hydrophobicity is characteristic of protein misfolding,[31] the native cell proteasome may recognize and degrade proteins tagged with the hydrophobic moiety. Taavi Neklesa and Craig Crews first reported hydrophobic tag degradation in 2011 as a tool to probe protein function in conjunction with cognate HaloTag fusion proteins.[32] This principle has also been further used to effectively degrade transcription factors[33] (a traditionally difficult class to drug[34]) and cancer-linked EZH2 in in vitro models.[35] As of yet, no drug candidates have been publicly identified making use of this technology.
Alternative strategies
Lysosome-targeting chimeras (LYTACs) have been developed, combining target-binding compounds or antibodies and glycopeptide ligands to stimulate the lysosomal degradation pathway. Unlike the proteasome pathway, this enables the targeted degradation of extracellular and membrane-bound proteins in addition to cytoplasmic ones.[36] Autophagy-targeting chimeras (AUTACs) can be employed to degrade proteins as well as protein aggregates and organelles.[37] AUTAC degradation tags are typically derived from guanine though the particular mechanism of action is still unclear.[38] Autophagosome-tethering compounds (ATTECs) mimic this strategy, directly appending a target protein to the autophagosome membrane for degradation absent the use of a linker.[39] Phosphorylation-inducing chimeric small molecules (PHICS) employ the warhead-linker-recruiter structure to direct phosphorylation of a given target by proximity to a desired kinase. This technique does not necessarily involve protein degradation and may instead be used to modulate protein function to direct or inhibit certain pathways.[40] Further work in the Crews Lab has used chimeric oligonucleotides, the dCas9 protein, and chimeric small molecules to create the TRAFTAC system for generalizable transcription factor degradation.[41]
Advantages
The ability to inhibit or modify enzyme function absent a catalytic pocket binding site target greatly expands the potentially druggable portion of the proteome.[42] Furthermore, most classes of chimeric small molecules can act on many targets over their life cycle,[43] lowering the effective dose compared to traditional inhibitors that act only on one protein at a time.[44] These therapeutics provide an alternative mechanism of action that may be useful as a combination therapy in diseases where drug resistance is a concern.[45] Chimeric drug activity is also highly dependent on distance between targeted proteins[46] allowing effect to be effectively tuned through optimization of the linker structure.
Challenges
The existence of two or more binding domains increases the difficulty of synthesis for chimeric molecules. Each component must be discovered, optimized, and synthesized in such a way that they can be linked together, driving up cost relative to single-domain inhibitors. The large size of chimeric molecules (typically 700-1100 Da) makes effective delivery difficult and increases complexity in pharmacokinetic design.[47][48] Care must be taken to ensure that the molecule is capable of passing through the cell membrane[49] and subsisting long enough to have therapeutic effect. Additionally, protein-protein ternary complexes are generally unstable, adding to the difficulty of chimeric drug design[50]
References
- ↑ Eladl O (September 2025). "Molecular glues and PROTACs in targeted protein degradation: mechanisms, advances, and therapeutic potential". Biochemical Pharmacology. 242 (Pt 3) 117297. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2025.117297. PMID 40907798.
- 1 2 3 Hinshaw SM, Banik SM, Gray NS (August 2025). "Generating Surprisingly Powerful Pharmacology from Chemically Induced Protein Interactions". Accounts of Chemical Research. 58 (15): 2394–2401. doi:10.1021/acs.accounts.5c00225. PMID 40705033.
- ↑ Yang Z, Xu J, Yang X, Chen J (August 2025). "Targeted protein degradation with small molecules for cancer immunotherapy". Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 20 (4) 101058. doi:10.1016/j.ajps.2025.101058. PMC 12337672. PMID 40791660.
- ↑ Kumar G, Thakur V, Sardana S, Tiwari V, Sharma D, Kumar A (August 2025). "Contemporary trends in targeted protein degradation for neurodegenerative diseases". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 300 118110. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2025.118110. PMID 40914014.
- ↑ Zhao L, Zhao J, Zhong K, Tong A, Jia D (April 2022). "Targeted protein degradation: mechanisms, strategies and application". Signal Transduction and Targeted Therapy. 7 (1) 113. doi:10.1038/s41392-022-00966-4. PMC 8977435. PMID 35379777.
- ↑ Veber DF, Johnson SR, Cheng HY, Smith BR, Ward KW, Kopple KD (June 2002). "Molecular properties that influence the oral bioavailability of drug candidates". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 45 (12): 2615–2623. doi:10.1021/jm020017n. PMID 12036371.
- ↑ Li Q, Kang C (July 2020). "Mechanisms of Action for Small Molecules Revealed by Structural Biology in Drug Discovery". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 21 (15): 5262. doi:10.3390/ijms21155262. PMC 7432558. PMID 32722222.
- ↑ Kana O, Brylinski M (May 2019). "Elucidating the druggability of the human proteome with eFindSite". Journal of Computer-Aided Molecular Design. 33 (5): 509–519. Bibcode:2019JCAMD..33..509K. doi:10.1007/s10822-019-00197-w. PMC 6516084. PMID 30888556.
- 1 2 Li H, Dong J, Cai M, Xu Z, Cheng XD, Qin JJ (September 2021). "Protein degradation technology: a strategic paradigm shift in drug discovery". Journal of Hematology & Oncology. 14 (1): 138. doi:10.1186/s13045-021-01146-7. PMC 8419833. PMID 34488823. S2CID 237418638.
- 1 2 3 Lai AC, Crews CM (February 2017). "Induced protein degradation: an emerging drug discovery paradigm". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 16 (2): 101–114. doi:10.1038/nrd.2016.211. PMC 5684876. PMID 27885283.
- ↑ Sakamoto KM, Kim KB, Kumagai A, Mercurio F, Crews CM, Deshaies RJ (July 2001). "Protacs: chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation". Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 98 (15): 8554–8559. Bibcode:2001PNAS...98.8554S. doi:10.1073/pnas.141230798. PMC 37474. PMID 11438690.
- ↑ Bouchie A, Allison M, Webb S, DeFrancesco L (March 2014). "Nature Biotechnology's academic spinouts of 2013". Nature Biotechnology. 32 (3): 229–238. doi:10.1038/nbt.2846. PMID 24727773. S2CID 692896.
- ↑ "PROTAC Protein Degrader Pipeline". Arvinas. Retrieved 2023-04-14.
- ↑ "Pfizer Strengthens Cancer Standing with Protein Degrader Collaboration". BioSpace. 22 July 2021. Retrieved 2023-04-14.
- ↑ "PROTAC Degraders in Clinical Trails: 2025 Update". Biopharma PEG. 2025-05-13. Retrieved 4 October 2025.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT03888612 for "Trial of ARV-110 in Patients With Metastatic Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer (mCRPC) " at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT05654623 for "A Study to Learn About a New Medicine Called Vepdegestrant (ARV-471, PF-07850327) in People Who Have Advanced Metastatic Breast Cancer (VERITAC-2) " at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT05067140 for "A Study of ARV-766 Given by Mouth in Men With Metastatic Prostate Cancer" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT05006716 for "A Dose-Escalation and Expansion Study of BGB-16673 in Participants With B-Cell Malignancies (CaDAnCe-101) " at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT04830137 for "A Study of NX-2127 in Adults With Relapsed/Refractory B-cell Malignancies " at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT05131022 for "A Study of NX-5948 in Adults With Relapsed/Refractory B-cell Malignancies " at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Naito M, Ohoka N, Shibata N (April 2019). "SNIPERs-Hijacking IAP activity to induce protein degradation". Drug Discovery Today. Technologies. 31: 35–42. doi:10.1016/j.ddtec.2018.12.002. PMID 31200857.
- ↑ Wang C, Zhang Y, Shi L, Yang S, Chang J, Zhong Y, et al. (December 2022). "Recent advances in IAP-based PROTACs (SNIPERs) as potential therapeutic agents". Journal of Enzyme Inhibition and Medicinal Chemistry. 37 (1): 1437–1453. doi:10.1080/14756366.2022.2074414. PMC 9122363. PMID 35589670.
- ↑ Darling S, Bajrami I, West SC (October 2025). "From serendipity to strategy: molecular glue degraders in cancer therapeutics". Critical Reviews in Biochemistry and Molecular Biology: 1–31. doi:10.1080/10409238.2025.2564068. PMID 41032400.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT04975997 for "Open-label Study Comparing Iberdomide, Daratumumab and Dexamethasone (IberDd) Versus Daratumumab, Bortezomib, and Dexamethasone (DVd) in Participants With Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (RRMM) (EXCALIBER-RRMM)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT05552976 for "A Study to Evaluate Mezigdomide in Combination With Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone (MeziKD) Versus Carfilzomib and Dexamethasone (Kd) in Participants With Relapsed or Refractory Multiple Myeloma (SUCCESSOR-2) (SUCCESSOR-2)" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT03834623 for "Avadomide (CC-122) in Combination With Nivolumab in Advanced Melanoma" at ClinicalTrials.gov
- ↑ He Q, Zhao X, Wu D, Jia S, Liu C, Cheng Z, et al. (November 2023). "Hydrophobic tag-based protein degradation: Development, opportunity and challenge". European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 260 115741. doi:10.1016/j.ejmech.2023.115741. PMID 37607438.
- ↑ Lai AC, Crews CM (February 2017). "Induced protein degradation: an emerging drug discovery paradigm". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 16 (2): 101–114. doi:10.1038/nrd.2016.211. PMC 5684876. PMID 27885283.
- ↑ Gheysen M, Punie K, Wildiers H, Neven P (November 2024). "Oral SERDs changing the scenery in hormone receptor positive breast cancer, a comprehensive review". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 130 102825. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2024.102825. PMID 39293125.
- ↑ Fredrickson EK, Rosenbaum JC, Locke MN, Milac TI, Gardner RG (July 2011). "Exposed hydrophobicity is a key determinant of nuclear quality control degradation". Molecular Biology of the Cell. 22 (13): 2384–2395. doi:10.1091/mbc.E11-03-0256. PMC 3128539. PMID 21551067.
- ↑ Neklesa TK, Tae HS, Schneekloth AR, Stulberg MJ, Corson TW, Sundberg TB, et al. (July 2011). "Small-molecule hydrophobic tagging-induced degradation of HaloTag fusion proteins". Nature Chemical Biology. 7 (8): 538–543. doi:10.1038/nchembio.597. PMC 3139752. PMID 21725302.
- ↑ Choi SR, Wang HM, Shin MH, Lim HS (June 2021). "Hydrophobic Tagging-Mediated Degradation of Transcription Coactivator SRC-1". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 22 (12): 6407. doi:10.3390/ijms22126407. PMC 8232704. PMID 34203850.
- ↑ Lambert SA, Jolma A, Campitelli LF, Das PK, Yin Y, Albu M, et al. (February 2018). "The Human Transcription Factors". Cell. 172 (4): 650–665. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2018.01.029. PMID 29425488. S2CID 3599827.
- ↑ Ma A, Stratikopoulos E, Park KS, Wei J, Martin TC, Yang X, et al. (February 2020). "Discovery of a first-in-class EZH2 selective degrader". Nature Chemical Biology. 16 (2): 214–222. doi:10.1038/s41589-019-0421-4. PMC 6982609. PMID 31819273.
- ↑ Banik S, Pedram K, Wisnovsky S, Riley N, Bertozzi C (2019). "Lysosome Targeting Chimeras (LYTACs) for the Degradation of Secreted and Membrane Proteins | Biological and Medicinal Chemistry". ChemRxiv. Cambridge Open Engage. doi:10.26434/chemrxiv.7927061.v1. Retrieved 2023-04-14.
- ↑ Takahashi D, Moriyama J, Nakamura T, Miki E, Takahashi E, Sato A, et al. (December 2019). "AUTACs: Cargo-Specific Degraders Using Selective Autophagy". Molecular Cell. 76 (5): 797–810.e10. doi:10.1016/j.molcel.2019.09.009. PMID 31606272. S2CID 204546213.
- ↑ Ding Y, Fei Y, Lu B (July 2020). "Emerging New Concepts of Degrader Technologies". Trends in Pharmacological Sciences. 41 (7): 464–474. doi:10.1016/j.tips.2020.04.005. PMC 7177145. PMID 32416934.
- ↑ Li Z, Zhu C, Ding Y, Fei Y, Lu B (January 2020). "ATTEC: a potential new approach to target proteinopathies". Autophagy. 16 (1): 185–187. doi:10.1080/15548627.2019.1688556. PMC 6984452. PMID 31690177.
- ↑ Siriwardena SU, Munkanatta Godage DN, Shoba VM, Lai S, Shi M, Wu P, et al. (August 2020). "Phosphorylation-Inducing Chimeric Small Molecules". Journal of the American Chemical Society. 142 (33): 14052–14057. doi:10.1021/jacs.0c05537. PMID 32787262. S2CID 221125004.
- ↑ Samarasinghe KT, Jaime-Figueroa S, Burgess M, Nalawansha DA, Dai K, Hu Z, et al. (May 2021). "Targeted degradation of transcription factors by TRAFTACs: TRAnscription Factor TArgeting Chimeras". Cell Chemical Biology. 28 (5): 648–661.e5. doi:10.1016/j.chembiol.2021.03.011. PMC 8524358. PMID 33836141.
- ↑ Lu B, Ye J (October 2021). "Commentary: PROTACs make undruggable targets druggable: Challenge and opportunity". Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica. B. 11 (10): 3335–3336. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2021.07.017. PMC 8546888. PMID 34729320.
- ↑ Békés M, Langley DR, Crews CM (March 2022). "PROTAC targeted protein degraders: the past is prologue". Nature Reviews. Drug Discovery. 21 (3): 181–200. doi:10.1038/s41573-021-00371-6. PMC 8765495. PMID 35042991.
- ↑ Yao T, Xiao H, Wang H, Xu X (September 2022). "Recent Advances in PROTACs for Drug Targeted Protein Research". International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 23 (18) 10328. doi:10.3390/ijms231810328. PMC 9499226. PMID 36142231.
- ↑ Burke MR, Smith AR, Zheng G (2022). "Overcoming Cancer Drug Resistance Utilizing PROTAC Technology". Frontiers in Cell and Developmental Biology. 10 872729. doi:10.3389/fcell.2022.872729. PMC 9083012. PMID 35547806.
- ↑ Cyrus K, Wehenkel M, Choi EY, Han HJ, Lee H, Swanson H, et al. (February 2011). "Impact of linker length on the activity of PROTACs". Molecular BioSystems. 7 (2): 359–364. doi:10.1039/c0mb00074d. PMC 3835402. PMID 20922213.
- ↑ Cantrill C, Chaturvedi P, Rynn C, Petrig Schaffland J, Walter I, Wittwer MB (June 2020). "Fundamental aspects of DMPK optimization of targeted protein degraders". Drug Discovery Today. 25 (6): 969–982. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2020.03.012. PMID 32298797. S2CID 215803460.
- ↑ Pike A, Williamson B, Harlfinger S, Martin S, McGinnity DF (October 2020). "Optimising proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) for oral drug delivery: a drug metabolism and pharmacokinetics perspective". Drug Discovery Today. 25 (10): 1793–1800. doi:10.1016/j.drudis.2020.07.013. PMID 32693163. S2CID 220699596.
- ↑ Klein VG, Townsend CE, Testa A, Zengerle M, Maniaci C, Hughes SJ, et al. (September 2020). "Understanding and Improving the Membrane Permeability of VH032-Based PROTACs". ACS Medicinal Chemistry Letters. 11 (9): 1732–1738. doi:10.1021/acsmedchemlett.0c00265. PMC 7488288. PMID 32939229.
- ↑ Weiss DR, Bortolato A, Sun Y, Cai X, Lai C, Guo S, et al. (April 2023). "On Ternary Complex Stability in Protein Degradation: In Silico Molecular Glue Binding Affinity Calculations". Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling. 63 (8): 2382–2392. doi:10.1021/acs.jcim.2c01386. PMID 37037192. S2CID 258061404.