Rintodestrant
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | G1T48 |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
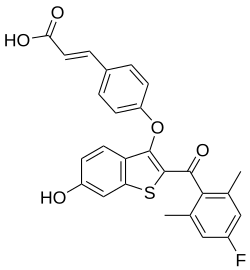
| Formula | C26H19FO5S |
| Molar mass | 462.49 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Rintodestrant (G1T48) is an orally bioavailable selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD) discovered in Greg Thatcher's lab at UIC[1] and developed by G1 Therapeutics for the treatment of estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer[2]. Structurally inspired by the 6-OH-benzothiophene scaffold used in arzoxifene and raloxifene, rintodestrant selectively binds to the estrogen receptor and inhibits ER signaling, demonstrating efficacy in endocrine-resistant tumors.[3]
A phase I clinical trial evaluated rintodestrant as monotherapy and in combination with the CDK4/6 inhibitor palbociclib in patients with ER+/HER2- advanced breast cancer.[4]
References
- ↑ Xiong R, Zhao J, Gutgesell LM, Wang Y, Lee S, Karumudi B, et al. (February 2017). "Novel Selective Estrogen Receptor Downregulators (SERDs) Developed against Treatment-Resistant Breast Cancer". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 60 (4): 1325–1342. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b01355. PMID 28117994.
- ↑ Andreano KJ, Wardell SE, Baker JG, Desautels TK, Baldi R, Chao CA, et al. (April 2020). "G1T48, an oral selective estrogen receptor degrader, and the CDK4/6 inhibitor lerociclib inhibit tumor growth in animal models of endocrine-resistant breast cancer". Breast Cancer Research and Treatment. 180 (3): 635–646. doi:10.1007/s10549-020-05575-9. PMC 7103015. PMID 32130619.
- ↑ Gheysen M, Punie K, Wildiers H, Neven P (November 2024). "Oral SERDs changing the scenery in hormone receptor positive breast cancer, a comprehensive review". Cancer Treatment Reviews. 130 102825. doi:10.1016/j.ctrv.2024.102825. PMID 39293125.
- ↑ Clinical trial number NCT03455270 for "G1T48, an Oral SERD, Alone and in Combination With Palbociclib in ER-Positive, HER2-Negative Advanced Breast Cancer" at ClinicalTrials.gov