Penoxsulam
 | |
| Names | |
|---|---|
| Preferred IUPAC name
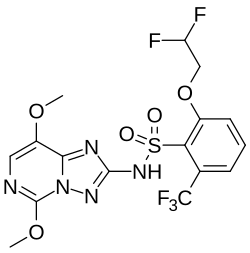
2-(2,2-Difluoroethoxy)-N-(5,8-dimethoxy-[1,2,4]triazolo[1,5-c]pyrimidin-2-yl)-6-(trifluoromethyl)benzenesulfonamide | |
| Identifiers | |
CAS Number |
|
3D model (JSmol) |
|
| ChEBI | |
| ChEMBL | |
| ChemSpider | |
| ECHA InfoCard | 100.107.359 |
| KEGG | |
PubChem CID |
|
| UNII | |
CompTox Dashboard (EPA) |
|
InChI
| |
SMILES
| |
| Properties | |
Chemical formula |
C16H14F5N5O5S |
| Molar mass | 483.37 g·mol−1 |
Except where otherwise noted, data are given for materials in their standard state (at 25 °C [77 °F], 100 kPa).
Infobox references | |
Penoxsulam is sulfonamide and triazolopyrimidine herbicide that acts as an acetolactate synthase inhibitor.[1][2] It is primarily used for rice production.[3]
Penoxsulam's HRAC classification is Group B (global, Aus), Group 2 (numeric), as it is an acetohydroxyacid synthase inhibitor.[4]
References
- ↑ European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) (April 2017). "Review of the existing maximum residue levels for penoxsulam according to Article 12 of Regulation (EC) No 396/2005". EFSA Journal. 15 (4): e04753. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2017.4753. PMC 7010082. PMID 32625459.
- ↑ "Pesticide Fact Sheet" (PDF). United States Environmental Protection Agency. Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- ↑ "Penoxsulam Considerations - Plant Management in Florida Waters - An Integrated Approach - University of Florida, Institute of Food and Agricultural Sciences - UF/IFAS". plants.ifas.ufl.edu. University of Florida. Retrieved 9 January 2024.
- ↑ "Classification of Herbicides According to Site of Action". Retrieved 19 July 2025.
External links
- Penoxsulam in the Pesticide Properties DataBase (PPDB)