Methanothermobacter
| Methanothermobacter | |
|---|---|
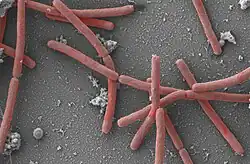 | |
| Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus | |
| Scientific classification | |
| Domain: | Archaea |
| Kingdom: | Methanobacteriati |
| Phylum: | Methanobacteriota |
| Class: | Methanobacteria |
| Order: | Methanobacteriales |
| Family: | Methanobacteriaceae |
| Genus: | Methanothermobacter Wasserfallen et al. 2000 |
| Type species | |
| Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus (Zeikus & Wolfe 1972) Wasserfallen et al. 2000 | |
| Species | |
| |
| Synonyms | |
| |
Methanothermobacter is a genus of archaeans in the family Methanobacteriaceae.[1] The species within this genus are thermophilic and grow best at temperatures between 55 °C and 65 °C. They are methanogens; they use carbon dioxide and hydrogen as substrates to produce methane for energy.[2]
Phylogeny
The currently accepted taxonomy is based on the List of Prokaryotic names with Standing in Nomenclature (LPSN)[3] and National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI).[1]
| 16S rRNA based LTP_06_2022[4][5][6] | 53 marker proteins based GTDB 10-RS226[7][8][9] | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
|
Metabolism
The metabolism of Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus has been reconstructed in the form of experimentally validated computer models for the two strains Z-245 and ΔH.[10]
See also
References
- 1 2 C.L. Schoch; et al. "Methanothermobacter". National Center for Biotechnology Information (NCBI) taxonomy database. Retrieved 2025-02-28.
- ↑ Stanley Falkow; Eugene Rosenberg; Karl-Heinz Schleifer; Erko Stackebrandt, eds. (2006-10-10). The Prokaryotes. Vol. 3. Springer Science & Business Media. p. 241. ISBN 0387254935. Retrieved 2016-08-30.
- ↑ Methanothermobacter in LPSN; Meier-Kolthoff, Jan P.; Sardà Carbasse, Joaquim; Peinado-Olarte, Rosa L.; Göker, Markus (7 January 2022). "TYGS and LPSN: a database tandem for fast and reliable genome-based classification and nomenclature of prokaryotes". Nucleic Acids Research. 50 (D1): D801 – D807. doi:10.1093/nar/gkab902.
- ↑ "The LTP". Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ↑ "LTP_all tree in newick format". Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ↑ "LTP_06_2022 Release Notes" (PDF). Retrieved 10 May 2023.
- ↑ "GTDB release 10-RS226". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 1 May 2025.
- ↑ "ar53_r226.sp_label". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 1 May 2025.
- ↑ "Taxon History". Genome Taxonomy Database. Retrieved 1 May 2025.
- ↑ Casini, Isabella; McCubbin, Tim; Esquivel-Elizondo, Sofia; Luque, Guillermo G.; Evseeva, Daria; Fink, Christian; Beblawy, Sebastian; Youngblut, Nicholas D.; Aristilde, Ludmilla; Huson, Daniel H.; Dräger, Andreas; Ley, Ruth E.; Marcellin, Esteban; Angenent, Largus T.; Molitor, Bastian (2023). "An integrated systems-biology approach reveals differences in formate metabolism in the genus Methanothermobacter". iScience. 26 (10). Bibcode:2023iSci...26j8016C. doi:10.1016/j.isci.2023.108016. PMC 10579436. PMID 37854702.
Further reading
Scientific journals
- Seifert, A.H.; Rittmann, S.; Herwig, C (20 July 2014). "Analysis of process related factors to increase volumetric productivity and quality of biomethane with Methanothermobacter marburgensis". Applied Energy. 132: 155–162. Bibcode:2014ApEn..132..155S. doi:10.1016/j.apenergy.2014.07.002.
- Wasserfallen A; Nolling J; Pfister P; Reeve J; et al. (2000). "Phylogenetic analysis of 18 thermophilic Methanobacterium isolates supports the proposals to create a new genus, Methanothermobacter gen. nov., and to reclassify several isolates in three species, Methanothermobacter thermautotrophicus comb. nov., Methanothermobacter wolfeii comb. nov. and Methanothermobacter marburgensis sp. nov". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 50: 43–53. doi:10.1099/00207713-50-1-43. PMID 10826786.
External links