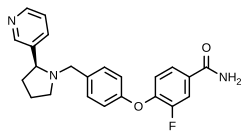
LY-2459989
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Routes of administration | Oral, intravenous |
| ATC code |
|
| Pharmacokinetic data | |
| Elimination half-life | 15 minutes (in rhesus monkeys)[1] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| UNII | |
| CompTox Dashboard (EPA) | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
| Formula | C23H22FN3O2 |
| Molar mass | 391.446 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
LY-2459989 is a silent antagonist of the κ-opioid receptor (KOR) that has been developed by Eli Lilly as a radiotracer of that receptor, labeled either with carbon-11[1] or fluorine-18.[2]
Pharmacology
Pharmacokinetics
LY-2459989 exhibits greatly improved central nervous system permeation relative to LY-2795050, with brain levels approximately six times higher than those of its predecessor.[1] The compound has a short duration of action, with only 25% of the compound remaining in serum 30 minutes post-injection in rhesus monkeys, making it an ideal agent for application in biomedical imaging, such as positron emission tomography (PET).[1]
Pharmacodynamics
LY-2459989 possesses high affinity for the KOR (Ki = 0.18 nM) and is highly selective for it over the μ-opioid receptor (Ki = 7.68 nM) and the δ-opioid receptor (Ki = 91.3 nM), showing over 43-fold selectivity for the KOR relative to the other opioid receptors.[1] LY-2459989 is a fluorine-containing analogue and follow-up compound of LY-2795050, the first KOR-selective antagonist radiotracer.[1] Relative to LY-2795050, LY-2459989 displays 4-fold higher affinity for the KOR and similar selectivity.[1]
Earlier analogues of LY-2459989 besides LY-2795050 with similar actions and potential uses have also been described.[4] Short-acting κ antagonists of this type have been shown to produce antidepressant-like effects in animal studies.[5]
See also
References
- 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 Zheng MQ, Kim SJ, Holden D, Lin SF, Need A, Rash K, et al. (July 2014). "An Improved Antagonist Radiotracer for the κ-Opioid Receptor: Synthesis and Characterization of (11)C-LY2459989". Journal of Nuclear Medicine. 55 (7): 1185–1191. doi:10.2967/jnumed.114.138701. PMC 4826283. PMID 24854795.
- ↑ Cai Z, Li S, Pracitto R, Navarro A, Shirali A, Ropchan J, et al. (January 2017). "Fluorine-18-Labeled Antagonist for PET Imaging of Kappa Opioid Receptors". ACS Chemical Neuroscience. 8 (1): 12–16. doi:10.1021/acschemneuro.6b00268. PMID 27741398.
- ↑ "LY-2795050". PubChem. U.S. National Library of Medicine.
- ↑ Mitch CH, Quimby SJ, Diaz N, Pedregal C, de la Torre MG, Jimenez A, et al. (December 2011). "Discovery of aminobenzyloxyarylamides as κ opioid receptor selective antagonists: application to preclinical development of a κ opioid receptor antagonist receptor occupancy tracer". Journal of Medicinal Chemistry. 54 (23): 8000–8012. doi:10.1021/jm200789r. PMID 21958337.
- ↑ Baynard C, Prisinzano TE, Butelman ER (2021). "Rapid-Onset Anti-Stress Effects of a Kappa-Opioid Receptor Antagonist, LY2795050, Against Immobility in an Open Space Swim Paradigm in Male and Female Mice". Frontiers in Pharmacology. 12 775317. doi:10.3389/fphar.2021.775317. PMC 8645979. PMID 34880762.