Dissimilatory sulfite reductase
| dissimilatory sulfite reductase | |||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Identifiers | |||||||||
| EC no. | 1.8.1.22 | ||||||||
| Databases | |||||||||
| IntEnz | IntEnz view | ||||||||
| BRENDA | BRENDA entry | ||||||||
| ExPASy | NiceZyme view | ||||||||
| KEGG | KEGG entry | ||||||||
| MetaCyc | metabolic pathway | ||||||||
| PRIAM | profile | ||||||||
| PDB structures | RCSB PDB PDBe PDBsum | ||||||||
| Gene Ontology | AmiGO / QuickGO | ||||||||
| |||||||||
Dissimilatory sulfite reductase (EC 1.8.1.22) is an enzyme that participates in sulfur metabolism in dissimilatory sulfate reduction.[1]
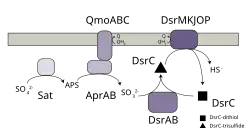
The enzyme is essential in prokaryotic sulfur-based energy metabolism, including sulfate/sulfite reducing organisms, sulfur-oxidizing bacteria, and organosulfonate reducers. In sulfur reducers, it catalyses the reduction of sulfite to sulfide (reaction 1); while in sulfur oxidizers, it catalyses the opposite reaction (reaction 2).[2] The reaction involves the small protein DsrC, which is present in all the organisms that contain dissimilatory sulfite reductase.[3] During the process, an intramolecular trisulfide is formed between two L-cysteine residues of DsrC and the sulfur atom from sulfite.[4] This trisulfide can be reduced by a number of proteins including DsrK and TcmB.[5]
DsrAB has been found in 32 bacterial and 4 to 5 archaeal phyla.[6] DsrA and DsrC have been found as auxiliary metabolic genes in bacteriophages.[7]
Reaction in organisms performing dissimilatory sulfate reduction:
SO2−3 + [DsrC]-(SH)2 + 2 acceptorred + 2H+ → H2S + [DsrC]-S2 + 2 acceptorox + 3H2O
SO2−3 + [DsrC]-(SH)2 + 2 acceptorred + 2H+ → [DsrC]-Cys-S-HS* + 2 acceptorox + 3H2O
[DsrC]-Cys-S-HS* → H2S + [DsrC]-S2
Reaction in organisms performing sulfur oxidation:
[DsrC]-Cys-S-HS* + 3 acceptorox + 3H2O → SO2−3 + [DsrC]-S2 + 3 acceptorred + 2H+
[DsrC]-Cys-S-HS* + 3 acceptorox + 3H2O → [DsrC]-Cys-S-SO3 + 3 acceptorred + H+
[DsrC]-Cys-S-SO3 → SO2−3 + [DsrC]-S2 + H+
The systematic name of this enzyme class is hydrogen-sulfide:[DsrC sulfur-carrier protein],acceptor oxidoreductase.
This enzyme is different from EC 1.8.1.2 – assimilatory sulfite reductase (NADPH), and EC 1.8.7.1 – assimilatory sulfite reductase (ferredoxin), which are involved in sulfate assimilation.
References
![]() This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license. BRENDA online database for enzymes: 1.8.1.22
This article incorporates text available under the CC BY 4.0 license. BRENDA online database for enzymes: 1.8.1.22
- ↑ Parey K, Warkentin E, Kroneck PM, Ermler U (October 2010). "Reaction cycle of the dissimilatory sulfite reductase from Archaeoglobus fulgidus". Biochemistry. 49 (41): 8912–21. doi:10.1021/bi100781f. PMID 20822098.
- ↑ Schedel M, Vanselow M, Trüper HG (1979). "Siroheme sulfite reductase isolated from Chromatium vinosum. Purification and investigation of some of its molecular and catalytic properties". Archives of Microbiology. 121 (1): 29–36. Bibcode:1979ArMic.121...29S. doi:10.1007/BF00409202. S2CID 22126920.
- ↑ Oliveira TF, Vonrhein C, Matias PM, Venceslau SS, Pereira IA, Archer M (December 2008). "The crystal structure of Desulfovibrio vulgaris dissimilatory sulfite reductase bound to DsrC provides novel insights into the mechanism of sulfate respiration". The Journal of Biological Chemistry. 283 (49): 34141–9. doi:10.1074/jbc.M805643200. PMC 2662231. PMID 18829451.
- ↑ Santos AA, Venceslau SS, Grein F, Leavitt WD, Dahl C, Johnston DT, Pereira IA (December 2015). "A protein trisulfide couples dissimilatory sulfate reduction to energy conservation". Science. 350 (6267): 1541–5. Bibcode:2015Sci...350.1541S. doi:10.1126/science.aad3558. PMID 26680199. S2CID 206643054.
- ↑ Venceslau SS, Stockdreher Y, Dahl C, Pereira IA (July 2014). "The "bacterial heterodisulfide" DsrC is a key protein in dissimilatory sulfur metabolism". Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Bioenergetics. 1837 (7): 1148–64. doi:10.1016/j.bbabio.2014.03.007. PMID 24662917.
- ↑ Mateos K, Chappell G, Klos A, Le B, Boden J, Stüeken E, Anderson R (July 2023). "The evolution and spread of sulfur cycling enzymes reflect the redox state of the early Earth". Science Advances. 9 (27) eade4847. doi:10.1126/sciadv.ade4847. hdl:10023/28108. PMID 37418533.
- ↑ Kieft K, Zhou Z, Anderson RE, Buchan A, Campbell BJ, Hallam SJ, Hess M, Sullivan MB, Walsh DA, Roux S, Anantharaman K (June 2021). "Ecology of inorganic sulfur auxiliary metabolism in widespread bacteriophages". Nature Communications. 12 3503. doi:10.1038/s41467-021-23698-5. PMC 8190135.