Cibinetide
 | |
| Clinical data | |
|---|---|
| Other names | ARA-290; ARA290; PHBSP; pHBSP peptide; pGlu-Glu-Gln-Leu-Glu-Arg-Ala-Leu-Asn-Ser-Ser; Pyroglutamate helix B surface peptide; UEQLERALNSS |
| Drug class | Erythropoietin receptor agonist[1][2] |
| Identifiers | |
IUPAC name
| |
| CAS Number | |
| PubChem CID | |
| DrugBank | |
| ChemSpider | |
| UNII | |
| KEGG | |
| ChEMBL | |
| Chemical and physical data | |
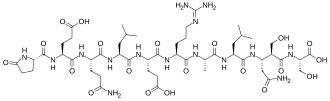
| Formula | C51H84N16O21 |
| Molar mass | 1257.324 g·mol−1 |
| 3D model (JSmol) | |
SMILES
| |
InChI
| |
Cibinetide (INN; USAN; developmental code name ARA-290) is an erythropoietin receptor agonist which is under development for the treatment of a variety of different medical conditions.[1][2][3][4] It was also under development for the treatment of depressive disorders, but development for this indication was discontinued.[1] The drug is under development by Araim Pharmaceuticals.[1][2] Modified derivatives with a longer duration of action have also been developed.[5]
References
- 1 2 3 4 "Cibinetide - Araim Pharmaceuticals". AdisInsight. 28 June 2022. Retrieved 23 October 2024.
- 1 2 3 "Delving into the Latest Updates on Cibinetide with Synapse". Synapse. 8 October 2024. Retrieved 23 October 2024.
- ↑ Peng B, Kong G, Yang C, Ming Y (February 2020). "Erythropoietin and its derivatives: from tissue protection to immune regulation". Cell Death Dis. 11 (2): 79. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-2276-8. PMC 6997384. PMID 32015330.
- ↑ Winicki NM, Nanavati AP, Morrell CH, Moen JM, Axsom JE, Krawczyk M, Petrashevskaya NN, Beyman MG, Ramirez C, Alfaras I, Mitchell SJ, Juhaszova M, Riordon DR, Wang M, Zhang J, Cerami A, Brines M, Sollott SJ, de Cabo R, Lakatta EG. A small erythropoietin derived non-hematopoietic peptide reduces cardiac inflammation, attenuates age associated declines in heart function and prolongs healthspan. Front Cardiovasc Med. 2023 Jan 18;9:1096887. doi:10.3389/fcvm.2022.1096887
{{doi}}: unflagged free DOI (link) PMID 36741836 - ↑ Liu G, Liang J, Li W, Jiang S, Song M, Xu S, Du Q, Wang L, Wang X, Liu X, Tang L, Yang Z, Zhou M, Meng H, Zhang L, Yang Y, Zhang B. The protective effect of erythropoietin and its novel derived peptides in peripheral nerve injury. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Sep 10;138:112452. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112452 PMID 38943972