Annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma
| Annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma | |
|---|---|
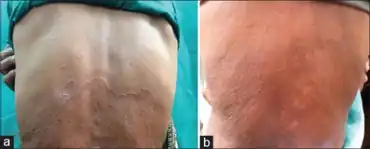 | |
| a) Annular elastolytic giant cell granuloma involving back b) regressed AEGCG lesions | |
Annular elastolytic giant-cell granuloma (also known as "Giant cell elastophagocytosis,"[1] "Meischer's granuloma,"[2] "Miescher's granuloma of the face"[1]) is a cutaneous condition characterized histologically by a dermal infiltrate of macrophages.[1][2]: 706
Localized granuloma annulare has a tendency towards spontaneous resolution. Localized lesions have been treated with potent topical corticosteroids.[3]
See also
References
- ↑ 1.0 1.1 1.2 Rapini, Ronald P.; Bolognia, Jean L.; Jorizzo, Joseph L. (2007). Dermatology: 2-Volume Set. St. Louis: Mosby. ISBN 978-1-4160-2999-1.
- ↑ 2.0 2.1 James, William D.; Berger, Timothy G.; et al. (2006). Andrews' Diseases of the Skin: clinical Dermatology. Saunders Elsevier. ISBN 978-0-7216-2921-6.
- ↑ Ruby Ghadially; Akos Z Szabo; Amit Garg (January 25, 2012). "Granuloma Annulare Treatment". Medscape. Archived from the original on September 16, 2017. Retrieved December 21, 2020. Archived September 16, 2017, at the Wayback Machine
External links
| Classification |
|---|