You can restrict access to your ssh server in many ways.
IMO the most important is to use ssh keys and disable password authentication.
See the following wiki pages for details
You can restrict access to a specific subnet in several ways. I will assume your ssh server is on subnet 192.168.0.0/16 with an ip address of 192.168.0.10 , adjust accordingly ;)
Router
One line of defense is to use a router. Be sure to disable UPnP and do not allow port forwarding.
SSH configuration
You can set several options in /etc/ssh/sshd_config. One is the listen address. If You set a listen address on your subnet. A private IP address is not routable over the internet.
ListenAddress 192.168.0.10
You can also use the AllowUsers
AllowUsers you@192.168.0.0/16
Somewhat related, you can also change the port
Port 1234
See: http://manpages.ubuntu.com/manpages/precise/man5/sshd_config.5.html
TCP wrapper
As outlined on the forums post, you can use TCP Wrapper . TCP wrapper uses 2 files, /etc/hosts.allow and /etc/hosts.deny
Edit /etc/hosts.allow and add your subnet
sshd : 192.168.0.
Edit /etc/hosts.deny , and deny all
ALL : ALL
See also: http://ubuntu-tutorials.com/2007/09/02/network-security-with-tcpwrappers-hostsallow-and-hostsdeny/
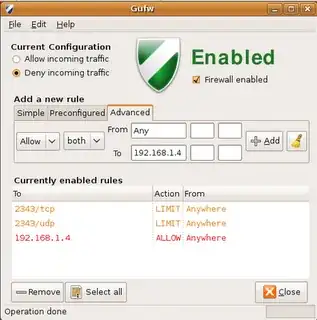
Firewall
Last you can firewall your server. You can use iptables, ufw, or gufw.
iptables
sudo iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -s 192.168.0.0/16 -j ACCEPT
sudo iptables -A INPUT -p tcp --dport 22 -j REJECT
Please do not use DROP in iptables.
ufw
sudo ufw allow from 192.168.0.0/16 to any port 22
ufw has a graphical interface: gufw