| Synpolydactyly |
|---|
|
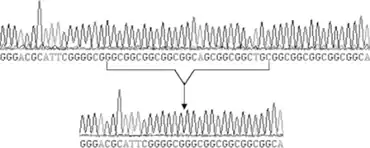 |
| Sequencing results of the HOXD13 gene from affected and unaffected individuals, compared with the reference HOXD13 gene sequence, the affected members all carried a 27-bp insertion, encoding nine additional alanines. |
 |
Synpolydactyly is a joint presentation of syndactyly (fusion of digits) and polydactyly (production of supernumerary digits). This is often a result of a mutation in the HOX D13 gene.[1]
Types
References
External links
|
|---|
| (1) Basic domains | |
|---|
(2) Zinc finger
DNA-binding domains | |
|---|
| (3) Helix-turn-helix domains | | 3.1 |
- ARX
- MNX1
- HOXD13
- PDX1
- LMX1B
- MSX1
- PITX2
- POU4F3
- POU3F4
- ZEB1
- ZEB2
|
|---|
| 3.2 |
- PAX2
- PAX3
- PAX4
- PAX6
- PAX8
- PAX9
|
|---|
| 3.3 | |
|---|
| 3.5 | |
|---|
|
|---|
(4) β-Scaffold factors
with minor groove contacts | |
|---|
| (0) Other transcription factors | |
|---|
| Ungrouped | |
|---|
| Transcription coregulators | |
|---|
